Functions of Dof transcription factors unique to plants
Approximately 5.9% of the total number of genes in Arabidopsis is estimated to encode transcription factors, and approximately 45% of Arabidopsis transcription factors are specific in plants without animal and yeast homologues. Genes encoding plant-specific transcription factors probably came into existence after the divergence of plants and animals, and then became involved in plant-specific biological processes.
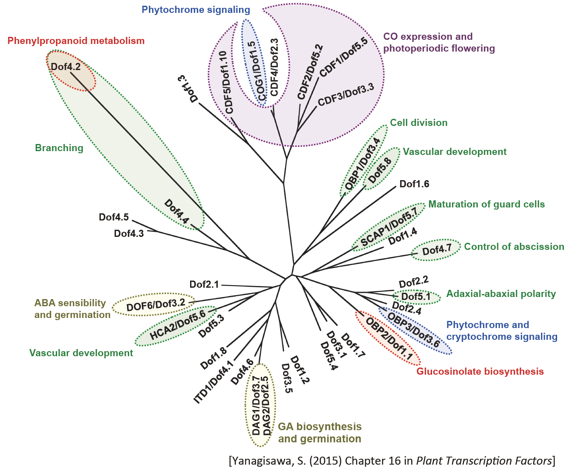
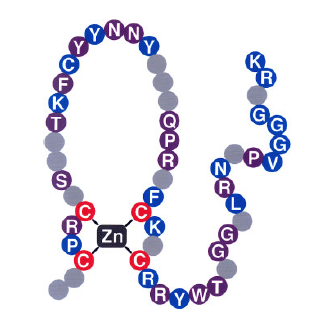
We identified a family of plant-specific transcription factors and named it the DNA-binding with one zinc finger (Dof) family (J. Biol. Chem. 268, 16028-16036, 1993; Nucleic Acid Res. 23, 3403-3410, 1995; Trends Plant Sci. 1, 213-214, 1996). Dof transcription factors possess a highly conserved DNA-binding domain (the Dof domain), which presumably forms a single C2-C2 zinc finger, and binds to the 5'-AAAG-3' or 5'-CTTT-3' sequence. Dof transcription factors have been found in angiosperms, moss, and alga, suggesting that Dof transcription factors are widely conserved in the plant kingdom (Trends Plant Sci. 7, 555-560, 2002; Plant Cell Physiol. 45, 386-391, 2004; Chapter 12 in Plant Transcription Factors, 2015). There are 36 Arabidopsis genes and a similar number of rice genes encoding Dof transcription factors, which have dramatically diverse physiological roles, including light regulation, circadian rhythm, seed-specific expression of storage protein genes, hormone response, guard cell development, and vascular development. The roles of many Dof family members remain to be elucidated. We are working to identify the role of each Dof transcription factor and the relationship between the Dof transcription factor family and transcriptional control in plants.
The Arabidopsis Information Resource
[Dof Arabidopsis gene family: see link ]
Publications (selected)
- Konishi, M., Donner, T., Scarpella, E., Yanagisawa, S. (2015) MONOPTEROS directly activates the auxin-inducible promoter of Dof5.8 transcription factor gene in Arabidopsis thaliana leaf provascular cells. J. Exp. Bot. 66: 283-291.
- Yanagisawa, S. (2015) Chapter 12: Structure and evolution of the plant Dof transcription factor family in Plant Transcription Factors: Evolutionary, Structural and Functional Aspects (Daniel H. Gonzalez, ed.), Elsevier/Academic Press, pp183-197.
- Negi, J., Moriwaki, K., Konishi, M., Yokoyama, R., Nakano, T., Kusumi, K., Hashimoto-Sugimoto, M., Schroeder, J.I., Nishitani, K., Yanagisawa, S., Iba, K. (2013) A Dof transcription factor, SCAP1, is essential for the development of functional stomata in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 23: 479-484.
- Sugiyama, T., Ishida, T., Tabei, N., T., Shigyo, M., Konishi M, Yoneyama, T., Yanagisawa, S. (2012) Involvement of PpDof1 transcriptional repressor in the nutrient condition-dependent growth control of protonemal filaments in Physcomitrella patens. J. Exp. Bot. 63: 3185-3197.
- Yanagisawa, S., Akiyama, A., Kisaka, H., Uchimiya, H., Miwa, T. (2004) Metabolic engineering with Dof1 transcription factor in plants: Improved nitrogen assimilation and growth under low nitrogen conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101: 7833-7838. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S. (2004) Dof domain proteins: Plant-specific transcription factors associated with diverse phenomena unique to plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 45: 386-391. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S. (2002) The Dof family of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 7: 555-560. [Abstract]
- Krohn N M, Yanagisawa S, Grasser K D (2002) Specificity of the stimulatory interaction between chromosomal HMGB proteins and the transcription factor Dof2 and its negative regulation by protein kinase CK2-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 32438-32444. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S. (2001) The transcriptional activation domain of the plant-specific Dof1 factor functions in plant, animal, and yeast cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 42: 813-822. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S. (2000) Dof1 and Dof2 transcription factors are associated with expression of multiple genes involved in carbon metabolism in maize. Plant J. 21: 281-288. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S, Schmidt R J. (1999) Diversity and similarity among recognition sequences of Dof transcription factors. Plant J. 17: 209-214. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S, Sheen J. (1998) Involvement of maize Dof zinc finger proteins in tissue-specific and light-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10: 75-89. [Abstract][Full Text][PDF (3.3 MB)]
- Yanagisawa S. (1997) Dof DNA-binding domains of plant transcription factors contribute to multiple protein- protein interactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 250: 403-410. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S. (1996) Dof DNA binding proteins contain a novel zinc finger motif. Trends Plant Sci. 1: 213-214.
- Yanagisawa S. (1995) A novel DNA binding domain that may form a single zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acid Res. 23: 3403-3410. [Abstract]
- Yanagisawa S, Izui K. (1993) Molecular cloning of two DNA binding proteins of maize that are structurally different but interact with the same sequence motif. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 16028-16036. [Abstract][Full Text PDF (6.8 MB)]