リン欠乏応答の制御メカニズム
リンは、窒素、カリウムとともに肥料の三要素です。植物はリン酸イ
オンとしてリンを獲得し、リン脂質や核酸の生合成に用いています。リン欠乏になると、植物はリン飢餓応
答性遺伝子を発現させるなどの生存戦略を取ります。この生存戦略で中心的役割を担う転写因子として
PHR1が知られています。体内のリンが十分な時には、PHR1はSPXタンパク質およびイノシトール
ポリリン酸と複合体を形成して不活化型となっていますが、リン欠乏状態になるとイノシトールポリリン酸
の濃度が低下して複合体からPHR1が遊離し、リン酸輸送体遺伝子などの発現が促進されることが知られ
ています。硝酸シグナル応答と硝酸欠乏応答を負に制御しているNIGT1とPHR1は構造的に近く、ま
た、認識する塩基配列も類似していることから(Plant Signal Behav.
8:e24447,
2013)、NIGT1遺伝子の自己抑制に関わるシスDNA配列をPHR1も認識して、硝酸イオンの獲得制御機構とリン酸イオンの獲得制御機構が一つに統
合されている可能性を考え、これを証明しました(Nat. Commun.
9:1376,
2018)。さらに、硝酸シグナルがNIGT1遺伝子を活性化し、これによってSPX遺伝子の発現を抑制してリン欠乏応答が強化されることも明らかにして
います(Plant J. 102:448-466, 2020)。
当研究室では、シロイヌナズナ野生系統間にみられるリン欠乏応答の遺伝的多様性に着目してリン欠乏応
答の制御に関わる因子の検索も行っています。その結果として、赤色光受容体(phytochrome
B)がリン欠乏応答に大きな影響を与えることを明らかにしています(Nat. Plants
4:1089-1101,
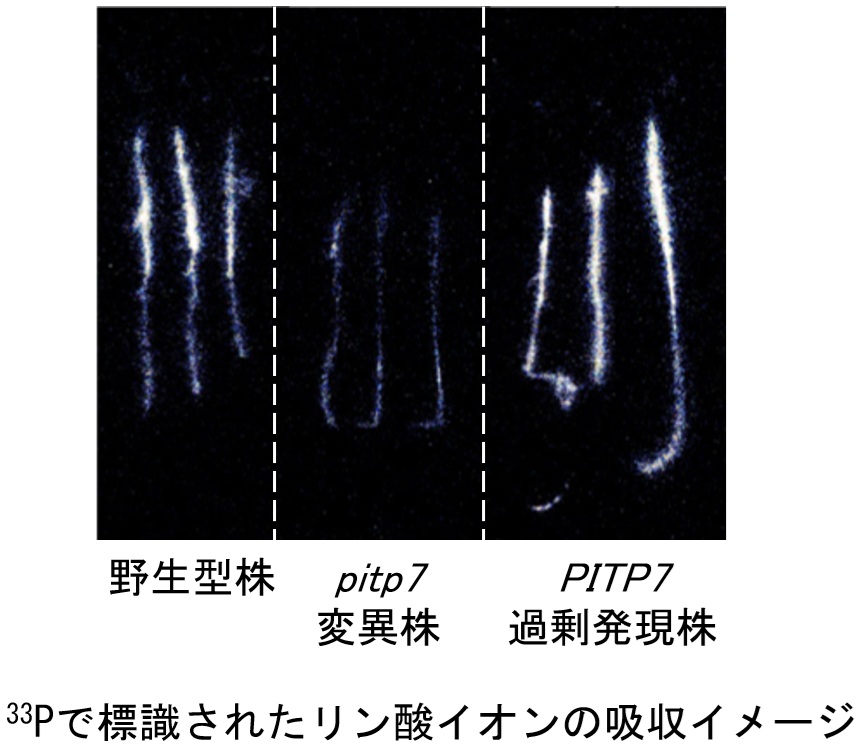
2018)。また、新奇なリン欠乏応答制御因子として、葉緑体局在型のSec14様タンパク質PITP7を同定しました。葉緑体局在型Sec14様タンパ
ク質のリン欠乏応答における役割はイネにおいても保存されており(Plant Physiol.
192:3030-3048,
2023)、リン欠乏応答やリン酸イオンの獲得制御と光合成活性の調節は密接に関わっていると考え、さらに研究を進めています。
関連する公表論文と総説
- Yang M, Sakuraba Y, Yanagisawa S. (2024) Down-regulation of the rice HRS1 HOMOLOG3 transcriptional repressor gene due to N deficiency directly co-activates ammonium and phosphate transporter genes. J. Exp. Bot. 76:461-477.
- Ohama N, Yanagisawa S. (2024) Role of GARP family transcription factors in the regulatory network for nitrogen and phosphorus acquisition. J Plant Res. 137:331-341.
- Yang M, Sakuraba Y, Ishikawa T, Ohtsuki N, Kawai-Yamada M, Yanagisawa, S. (2023) Chloroplastic Sec14-like proteins modulate growth and phosphate deficiency responses in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 192:3030-3048.
- Ueda Y, Sakuraba Y, Yanagisawa S. (2021) Environmental control of phosphorus acquisition: A piece of the molecular framework underlying nutritional homeostasis. Plant Cell Physiol. 62:573–581.
- Ueda Y, Nosaki S, Sakuraba Y, Miyakawa T, Kiba T, Tanokura M, Yanagisawa S. (2020) NIGT1 family proteins exhibit dual mode DNA recognition to regulate nutrient response-associated genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 16:e1009197.
- Ueda Y, Kiba T, Yanagisawa S. (2020) Nitrate-inducible NIGT1 proteins modulate phosphate uptake and starvation signaling via transcriptional regulation of SPX genes. Plant J. 102:448-466.
- Sakuraba Y, Yanagisawa S. (2020) Effect of phytochrome-mediated red light signaling on phosphorus uptake and accumulation in rice. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 66:745-754.
- Ueda Y, Yanagisawa S. (2019) Perception, transduction and integration of nitrogen and phosphorus nutritional signals in the transcriptional regulatory network in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 70:3709–3717.
- Sakuraba Y, Yanagisawa S. (2018) Light signalling-induced regulation of nutrient acquisition and utilisation in plants. Environmental sensing and plant development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 83:123-132.
- Sakuraba Y, Kanno S, Mabuchi A, Monda K, Iba K, Yanagisawa S. (2018) A phytochrome B-mediated regulatory mechanism of phosphorus acquisition. Nat. Plants 4:1089-1101.
- Maeda Y, Konishi M, Kiba T, Sakuraba Y, Sawaki N, Kurai T, Ueda Y, Sakakibara H, Yanagisawa S. (2018) A NIGT1-centered transcriptional cascade regulates nitrate signalling and incorporates phosphorus starvation signals in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 9:1376.
- Yanagisawa S. (2013) Characterization of a nitrate-inducible transcriptional repressor NIGT1 provides new insights into DNA recognition by the GARP family proteins. Plant Signal Behav. 8:e24447.